A Complete Guide to Varicose Veins in 2026 Understand symptoms, causes, and treatment paths. Learn more inside.
Varicose veins affect millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort, visible changes to the legs, and sometimes serious health concerns. These enlarged, twisted veins often appear blue or dark purple and can lead to symptoms like aching, heaviness, swelling, and fatigue. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing early symptoms, and exploring available treatment options are essential steps toward managing this common vascular condition effectively and improving quality of life.
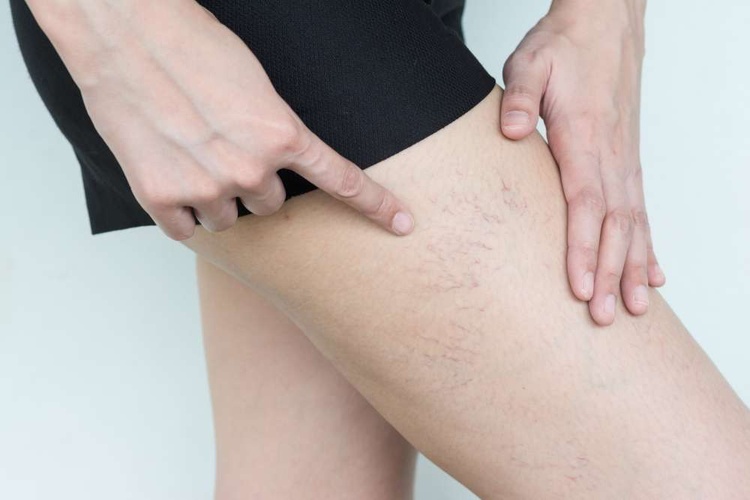
Varicose veins develop when the valves inside veins weaken or fail, causing blood to pool rather than flow efficiently back to the heart. This pooling leads to vein enlargement and the characteristic bulging appearance. Risk factors include age, genetics, prolonged standing or sitting, pregnancy, obesity, and hormonal changes. While varicose veins are often considered a cosmetic concern, they can also signal underlying circulatory issues and may lead to complications if left untreated.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Symptoms vary from mild to severe and may include visible, twisted veins beneath the skin, aching or throbbing pain in the legs, swelling around the ankles and feet, muscle cramps, itching around affected veins, and skin discoloration. Some individuals experience restless legs, especially after prolonged periods of standing. Symptoms often worsen during warm weather or after long hours on your feet. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent progression and reduce the risk of complications such as ulcers or blood clots.
What Causes Varicose Veins to Develop
Veins contain one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood accumulates in the vein, causing it to enlarge. Age is a significant factor, as vein walls and valves naturally weaken over time. Genetics also play a role; if family members have varicose veins, your risk increases. Pregnancy increases blood volume and hormonal changes can relax vein walls. Occupations requiring long periods of standing or sitting reduce circulation and increase vein pressure. Obesity adds extra strain on the veins, and hormonal treatments or menopause can also contribute to vein weakness.
Modern Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
Treatment has evolved significantly, with many non-surgical and minimally invasive approaches now available. Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution into the vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time. Endovenous laser therapy uses laser energy delivered through a thin fiber inserted into the vein, sealing it from the inside. Radiofrequency ablation works similarly, using heat generated by radiofrequency waves. Foam sclerotherapy is effective for larger veins and involves injecting a foam solution. VenaSeal is a newer technique using medical adhesive to close veins. Ambulatory phlebectomy removes veins through tiny incisions under local anesthesia. These procedures typically require minimal downtime and are performed in outpatient settings, offering effective alternatives to traditional vein stripping surgery.
Varicose Veins Treatment Offers to Know
Many clinics and medical centers provide consultation packages, seasonal promotions, and bundled treatment programs to make care more accessible. Initial consultations often include diagnostic imaging such as ultrasound to assess vein health and determine the most suitable treatment plan. Some facilities offer free or discounted consultations during certain months or as part of awareness campaigns. Bundled packages may combine multiple treatment sessions at a reduced rate, particularly for patients requiring treatment on both legs or multiple veins. Payment plans and financing options are increasingly available, allowing patients to manage costs over time. It is important to verify the credentials of the clinic, the experience of the specialists, and the technologies used before committing to any program.
| Provider Type | Services Offered | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vascular Surgery Centers | Sclerotherapy, laser therapy, radiofrequency ablation | Specialized equipment, experienced vascular surgeons, comprehensive diagnostics |
| Dermatology Clinics | Cosmetic sclerotherapy, laser treatments | Focus on aesthetic outcomes, outpatient procedures, minimal downtime |
| General Medical Clinics | Consultation, compression therapy, referrals | Initial assessment, conservative management, coordination with specialists |
| Mobile Vein Clinics | On-site consultations, basic treatments | Convenient access, community outreach, flexible scheduling |
Varicose Veins Tubes for Work, Travel & Daily Wear
Compression stockings or tubes are a cornerstone of varicose vein management and prevention. These garments apply graduated pressure to the legs, improving blood flow and reducing swelling and discomfort. They are especially beneficial for individuals who stand or sit for extended periods, such as healthcare workers, retail employees, office workers, and frequent travelers. Compression levels range from mild to extra firm, and a healthcare provider can recommend the appropriate level based on symptom severity. Modern designs are available in various styles, colors, and lengths, making them more discreet and comfortable for daily wear. Regular use can alleviate symptoms, prevent worsening, and support recovery after treatment procedures.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention Strategies
While some risk factors like genetics and age cannot be controlled, lifestyle modifications can reduce the likelihood of developing varicose veins or slow their progression. Regular physical activity, particularly walking, cycling, and swimming, promotes healthy circulation. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on leg veins. Elevating the legs when resting helps blood flow back toward the heart. Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, or taking breaks to move around, prevents blood from pooling. Wearing comfortable, supportive footwear and avoiding high heels can also help. A diet rich in fiber and low in salt supports vascular health and reduces fluid retention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While varicose veins are often manageable with conservative measures, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical evaluation. Persistent pain, significant swelling, skin changes such as discoloration or thickening, bleeding from a varicose vein, or the development of sores or ulcers near the affected area require professional assessment. These signs may indicate complications such as venous ulcers, superficial thrombophlebitis, or deep vein thrombosis. Early intervention can prevent serious health issues and improve treatment outcomes. A vascular specialist or phlebologist can perform diagnostic tests and recommend appropriate treatment based on individual needs.
Understanding varicose veins, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward better vascular health. With advances in minimally invasive procedures, supportive therapies like compression wear, and lifestyle adjustments, managing varicose veins has become more effective and accessible. Consulting a qualified healthcare provider ensures personalized care tailored to individual circumstances, helping to improve comfort, appearance, and overall well-being.




