Understanding Medicare Coverage for Hearing Aids
Medicare coverage for hearing aids has long been a complex topic for many seniors. With various parts of Medicare offering different levels of coverage and specific eligibility requirements, navigating the system can be challenging. This comprehensive guide explains what hearing aid benefits are available through Medicare, how to qualify, and what costs you might expect.
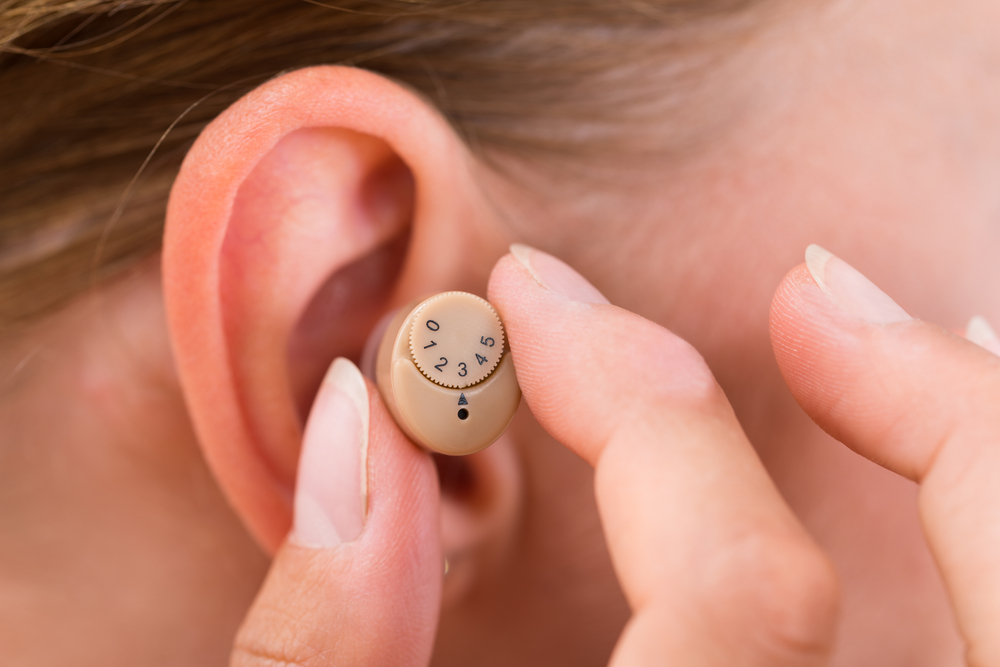

Medicare coverage for hearing aids represents an important consideration for millions of Americans with hearing loss. While Medicare’s relationship with hearing care has traditionally been limited, recent changes and various coverage options have created new possibilities for beneficiaries seeking hearing assistance. Understanding exactly what’s covered, what isn’t, and how to access benefits can significantly impact both your hearing health and financial planning.
What Hearing Aids Does Medicare Cover?
Traditional Medicare (Parts A and B) has historically provided very limited coverage for hearing-related services. Original Medicare does not cover routine hearing exams, hearing aids, or fittings for hearing aids. Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) will cover diagnostic hearing exams if your doctor orders them to determine whether you need medical treatment, but not routine hearing assessments.
The Medicare Modernization Act of 2003 specifically excludes hearing aids from coverage under Part B. This exclusion has been a longstanding limitation, leaving many beneficiaries to seek alternative funding sources for these often expensive devices.
However, some Medicare Advantage plans (Part C) offered by private insurance companies do include hearing benefits. These plans must provide at least the same coverage as Original Medicare, but many offer additional benefits, including some level of hearing aid coverage.
How Medicare Hearing Aid Benefits Work
Medicare Advantage plans that include hearing benefits typically operate through networks of providers. These plans may cover:
- Routine hearing exams
- Hearing aid fittings and evaluations
- Partial or complete coverage for hearing aid devices
- Maintenance and follow-up appointments
The specifics of coverage vary significantly between different Medicare Advantage providers and plans. Some plans may offer an allowance toward hearing aids (such as $500-$3,000 per ear every few years), while others might provide discounts through specific providers or hearing aid brands.
To use these benefits, you typically need to: 1. Confirm your plan includes hearing benefits 2. Visit in-network providers to maximize coverage 3. Obtain proper referrals if required by your plan 4. Follow the plan’s process for obtaining authorization
It’s important to understand that even with Medicare Advantage plans that offer hearing benefits, you may still have significant out-of-pocket costs depending on the type and technology level of hearing aids you choose.
Eligibility and Coverage Details
Eligibility for Medicare hearing aid benefits depends primarily on your enrollment in a Medicare Advantage plan that offers these benefits. To qualify:
- You must be enrolled in Medicare Parts A and B
- You must join a Medicare Advantage plan that includes hearing benefits
- You must follow the plan’s rules regarding network providers and referrals
Some plans have waiting periods before you can access hearing aid benefits, often ranging from 6-12 months after enrollment. Additionally, most plans limit how frequently you can receive new hearing aids, typically every 3-5 years.
Coverage details vary widely between plans, with some important considerations:
- Benefit caps: Most plans set maximum dollar amounts they’ll pay toward hearing aids
- Technology tiers: Higher technology hearing aids often require larger out-of-pocket payments
- Provider restrictions: Benefits may be limited to specific hearing aid brands or providers
- Replacement policies: Coverage for lost or damaged hearing aids varies significantly
It’s crucial to carefully review your plan’s Evidence of Coverage document to understand the specific hearing benefits available to you.
Types and Costs of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids come in various styles and technology levels, with corresponding price differences. Common styles include:
- Behind-the-ear (BTE): Sits behind the ear with a tube connecting to an earpiece
- In-the-ear (ITE): Custom-made to fill the outer ear
- In-the-canal (ITC): Smaller devices that fit partly in the ear canal
- Completely-in-canal (CIC): Nearly invisible devices that fit deep in the ear canal
- Receiver-in-canal (RIC): Similar to BTE but with the speaker in the ear canal
Technology levels typically range from basic to premium, with features like background noise reduction, directional microphones, Bluetooth connectivity, and rechargeability adding to the cost.
| Hearing Aid Type | Average Cost Per Aid | Common Features | Typical Medicare Advantage Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Technology | $1,000-$1,500 | Amplification, some noise reduction | Often covered with minimal copay |
| Mid-Range Technology | $1,500-$2,500 | Better noise reduction, some directionality | Partially covered with moderate copay |
| Premium Technology | $2,500-$4,000+ | Advanced noise reduction, Bluetooth, rechargeability | Limited coverage with higher copay |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How to Get Tested and Apply for Coverage
The process for accessing hearing aid benefits through Medicare typically begins with a hearing evaluation. Here’s how to navigate the process:
-
Medical clearance: First, visit your primary care physician to rule out medical causes of hearing loss that might require treatment rather than amplification.
-
Diagnostic hearing test: If medically necessary, Medicare Part B will cover this evaluation when ordered by your doctor.
-
Routine hearing assessment: If you have a Medicare Advantage plan with hearing benefits, schedule an appointment with an in-network audiologist or hearing instrument specialist for a comprehensive hearing evaluation.
-
Benefit verification: Work with your provider to verify your specific hearing aid benefits and coverage levels.
-
Selection and fitting: Choose appropriate hearing aids based on your hearing loss, lifestyle needs, and coverage limitations.
-
Follow-up care: Attend all recommended follow-up appointments to ensure proper adjustment and benefit from your hearing aids.
Most Medicare Advantage plans require you to use in-network providers to receive maximum benefits. Some plans may also require prior authorization or referrals before covering hearing services or devices.
If your Medicare plan doesn’t provide adequate hearing aid coverage, you might consider other funding sources such as veterans benefits, vocational rehabilitation services, or nonprofit organizations that provide assistance for hearing aids.
Understanding your Medicare hearing benefits requires careful review of your specific plan documents. While Original Medicare provides limited coverage, Medicare Advantage plans offer varying levels of hearing benefits that can significantly reduce out-of-pocket costs for hearing aids. By researching your options and working closely with healthcare providers, you can make informed decisions about addressing your hearing health needs while managing costs effectively.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.