A Practical Guide to Choosing the Right Hearing Aid for Your Needs
Selecting the right hearing aid can be a life-changing decision for those experiencing hearing loss. With numerous options available in today's market, the process might seem overwhelming at first. Hearing aids vary significantly in style, technology, features, and price points—each designed to address different types of hearing loss and personal preferences. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential factors to consider when choosing a hearing aid that best suits your unique needs, lifestyle, and hearing goals.
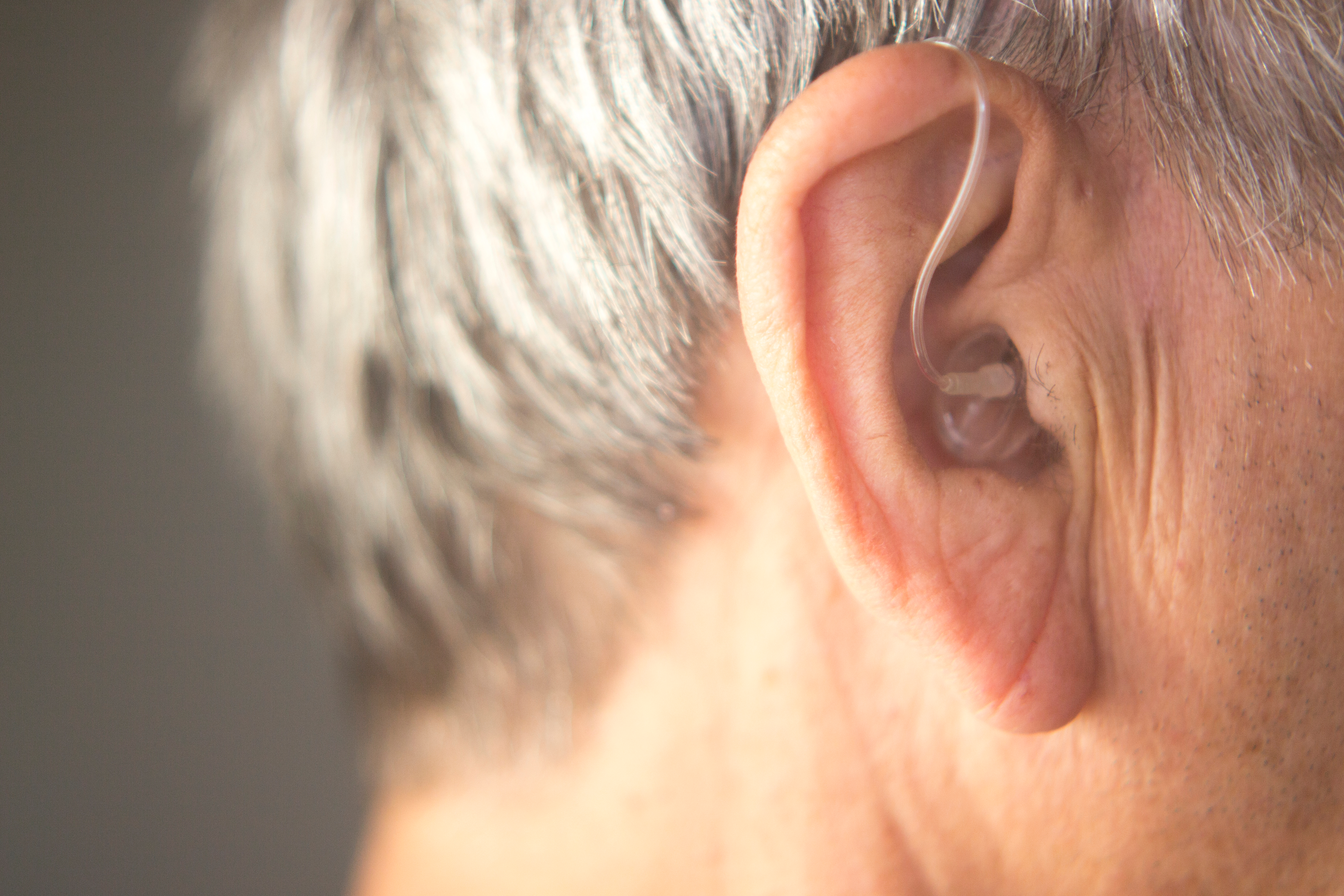
Understanding Hearing Aid Types and Styles
Hearing aids come in several distinct styles, each with its own advantages and limitations. Behind-the-ear (BTE) models hook over the top of your ear and rest behind it, connecting to a custom earpiece that fits in your ear canal. These are typically more powerful and easier to handle. In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids fit completely inside the outer ear and are suitable for mild to severe hearing loss. For those seeking discretion, completely-in-the-canal (CIC) and invisible-in-canal (IIC) devices sit deep within the ear canal, making them nearly invisible but potentially more difficult to adjust and remove.
Receiver-in-canal (RIC) and receiver-in-the-ear (RITE) models have gained popularity for their balanced approach, offering a combination of power, comfort, and relatively discreet appearance. The hearing aid type you choose should depend on your degree of hearing loss, manual dexterity, cosmetic preferences, and specific features needed. Your audiologist can help determine which style will best address your particular hearing challenges while aligning with your personal preferences.
Key Features and Technology Considerations
Modern hearing aids offer remarkable technological advancements that dramatically improve sound quality and user experience. Directional microphones help focus on sounds coming from in front of you while reducing background noise—particularly valuable in crowded environments. Noise reduction algorithms work continuously to decrease unwanted ambient sounds while preserving speech clarity. Feedback cancellation prevents the uncomfortable whistling that once plagued hearing aid users.
Wireless connectivity has revolutionized hearing aid functionality, allowing direct streaming from smartphones, televisions, and other devices. Many hearing aids now offer smartphone apps for discreet adjustments and personalized settings for different environments. When evaluating features, consider which technological capabilities will most impact your daily activities and communication needs. Some users prioritize natural sound quality, while others need specialized features for specific challenging environments like restaurants or outdoor settings.
Personal Lifestyle and Hearing Goals
Your daily activities and environments should significantly influence your hearing aid selection. If you lead an active lifestyle with exercise, consider water and dust-resistant models with secure fit options. For frequent phone users or music lovers, direct Bluetooth streaming capabilities provide convenience and enhanced listening experiences. Those in demanding work environments with frequent meetings or presentations might benefit from advanced directional microphones and speech enhancement features.
Defining clear hearing goals is essential—whether you primarily want to hear conversations in quiet settings, participate fully in noisy social gatherings, or enjoy music with greater fidelity. Be honest with your audiologist about your typical daily activities, hobbies, and situations where hearing clearly is most important to you. This information helps them recommend appropriate technology levels and features that align with your specific needs rather than unnecessary premium features you may never use.
Fitting, Adjustments, and Ongoing Care
The fitting process is critical for hearing aid success and typically involves multiple appointments. During initial fitting, your audiologist will program your devices based on your hearing test results and make physical adjustments to ensure comfort. Many users require follow-up appointments for fine-tuning as they adapt to hearing aids in real-world environments. Modern hearing aids often allow remote adjustments through smartphone apps, reducing the need for in-person visits for minor tweaks.
Proper maintenance extends your hearing aids’ lifespan and maintains optimal performance. Daily cleaning with appropriate tools, regular professional cleanings, and prompt attention to any issues are essential parts of hearing aid care. Most manufacturers offer warranties covering repairs and sometimes loss for 1-3 years. Consider ongoing costs such as batteries (if not rechargeable), cleaning supplies, and possible repair needs beyond the warranty period when budgeting for your hearing solution.
Understanding Hearing Aid Costs and Options
Hearing aids typically range from $1,000 to $4,000 per ear, varying based on technology level, features, and provider services. Entry-level devices offer basic amplification and minimal features, while premium models include advanced sound processing, connectivity options, and sophisticated algorithms. Most audiologists offer several technology tiers to accommodate different budgets and needs.
| Technology Level | Typical Price Range (per aid) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | $1,000-$1,600 | Essential amplification, minimal noise reduction, manual controls |
| Mid-Range | $1,600-$2,500 | Better noise reduction, directional microphones, some connectivity |
| Premium | $2,500-$4,000+ | Advanced sound processing, full wireless connectivity, automatic adjustments |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Many insurance plans provide limited or no coverage for hearing aids, though some offer partial reimbursement. Medicare typically doesn’t cover hearing aids, but Medicare Advantage plans might include some benefits. Veterans may qualify for free or discounted devices through VA benefits. Some states mandate insurance coverage for children’s hearing aids. Financing options, discount programs, and refurbished devices can make hearing solutions more accessible for those with budget constraints.
Making Your Final Decision
Selecting the right hearing aid ultimately requires balancing technology needs, personal preferences, and financial considerations. Many providers offer trial periods of 30-60 days, allowing you to test devices in your everyday environments before making a final commitment. Take advantage of this opportunity to evaluate how well the hearing aids perform in the situations most important to you. Don’t hesitate to request adjustments during this period—proper programming significantly impacts performance and satisfaction.
Remember that adapting to hearing aids takes time, as your brain needs to relearn how to process sounds you may not have heard clearly for years. Maintain realistic expectations and commit to consistent use to achieve the best outcomes. Working closely with a trusted audiologist who provides comprehensive follow-up care often leads to greater success and satisfaction with your hearing aids long-term.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.