Backyard Conservatories: Models, Different Payment Options, And Types Of Materials
Backyard conservatories are elegant additions to homes, offering a blend of indoor comfort and outdoor charm. These versatile structures provide a unique space to enjoy nature year-round, serving as sunrooms, greenhouses, or simply cozy retreats. As the popularity of conservatories continues to grow, homeowners are faced with various options in terms of models, materials, and financing. This article delves into the world of backyard conservatories, exploring the different styles available, payment solutions, and the materials that bring these stunning structures to life.
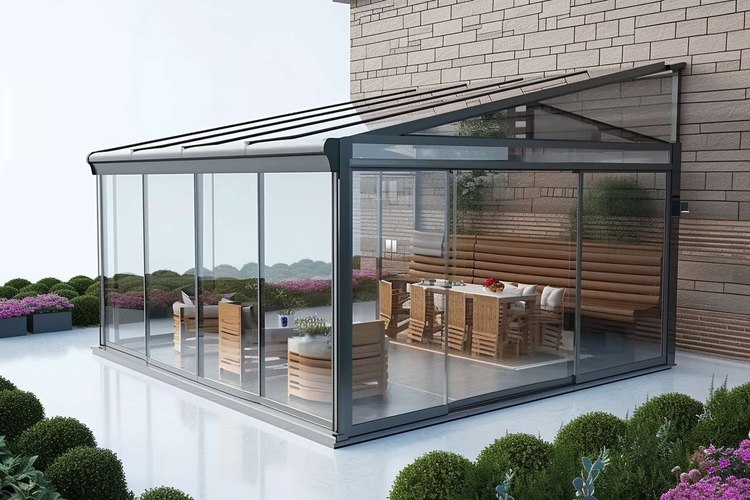

What Models of Backyard Conservatories Are There?
Backyard conservatories come in a variety of models, each designed to complement different architectural styles and personal preferences. The Victorian model is perhaps the most iconic, featuring ornate details and a pitched roof. Its classic design includes intricate ridge cresting and finials, making it a popular choice for traditional homes.
For those seeking a more contemporary look, the Lean-to model offers a sleek, minimalist design. This style is characterized by its single-sloped roof that extends from the house, making it ideal for properties with limited space or height restrictions.
The Edwardian model combines elegance with practicality, boasting a rectangular floor plan that maximizes usable space. Its pitched roof and clean lines make it versatile enough to suit both modern and traditional homes.
Gable-front conservatories feature a symmetrical pitched roof that forms a triangle at the front, creating a sense of height and grandeur. This model is particularly well-suited to larger properties and those looking to make a bold architectural statement.
What Payment Options Are Available for Backyard Conservatories?
Financing a backyard conservatory can be approached in several ways, depending on your budget and financial situation. Many homeowners opt for cash payments, especially for smaller projects, as this avoids interest charges and additional fees.
For those who prefer to spread the cost, personal loans are a popular choice. These unsecured loans typically offer fixed interest rates and repayment terms, allowing for easier budgeting. Home equity loans or lines of credit are another option, often providing lower interest rates due to the use of your home as collateral.
Some conservatory companies offer in-house financing options, which can include low or zero-interest periods for qualified buyers. These deals can be attractive but require careful consideration of the long-term costs and terms.
For energy-efficient conservatories, homeowners might qualify for green home improvement loans or government incentives, potentially reducing the overall cost of the project.
| Payment Option | Features | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Payment | No interest, immediate ownership | Large upfront cost |
| Personal Loan | Fixed terms, quick approval | Higher interest rates |
| Home Equity Loan | Lower interest rates, tax-deductible interest | Uses home as collateral |
| Company Financing | Potential for low or zero interest periods | Long-term costs may be higher |
| Green Home Loans | Possible incentives for energy efficiency | May have specific qualifying criteria |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
What Kind of Materials Are Used for Conservatories and What Are The Differences?
The choice of materials for a conservatory significantly impacts its appearance, durability, and maintenance requirements. uPVC (unplasticized polyvinyl chloride) is a popular option due to its affordability and low maintenance. It offers good insulation properties and comes in various colors and wood-effect finishes. However, it may not be as aesthetically pleasing as other materials and can discolor over time.
Aluminum conservatories provide a modern, sleek look with slim frames that maximize glass area. They are strong, durable, and require minimal maintenance. While initially more expensive than uPVC, aluminum’s longevity can make it cost-effective in the long run.
Timber conservatories offer timeless beauty and excellent insulation properties. Hardwoods like oak or mahogany provide durability and a luxurious appearance but require regular maintenance to prevent weathering and rot. Engineered timber offers improved stability and resistance to warping, making it a popular alternative to traditional wood.
For the glazing, double or triple-paned glass is standard, offering improved insulation and noise reduction compared to single-pane options. Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass coatings can further enhance energy efficiency by reflecting heat back into the conservatory during colder months.
Polycarbonate roofing is a lightweight and cost-effective alternative to glass for conservatory roofs. While not as visually appealing or insulating as glass, it provides good UV protection and is less prone to breakage.
When selecting materials for your backyard conservatory, consider factors such as your local climate, the conservatory’s intended use, and your home’s architectural style. Each material offers unique benefits, and the right choice will depend on your specific needs, budget, and aesthetic preferences.
In conclusion, backyard conservatories offer a wide range of models, payment options, and materials to suit various tastes and budgets. By carefully considering these factors, homeowners can create a beautiful and functional space that enhances their property and lifestyle for years to come.