Welding Machines options
Welding machines are used in a wide range of projects, from industrial work to home repairs. This article explores how they function, the types available, and how beginners are safely learning to use them in workshops or at home with the right equipment and training.
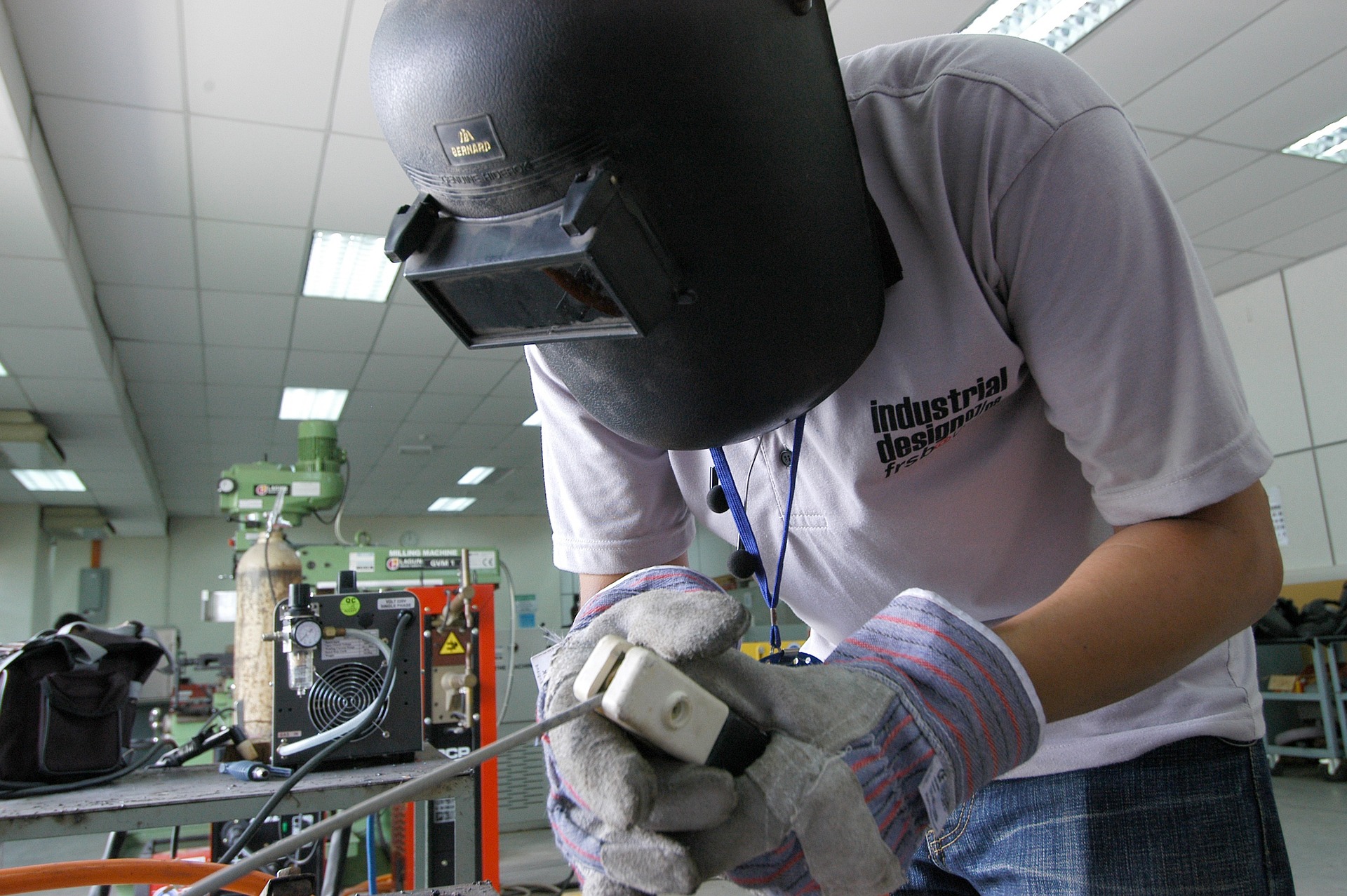

Common Types of Industrial Welding Tools
The welding industry offers several machine categories, each designed for specific applications. MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welders are popular for their versatility and ease of use, making them ideal for both thin and thick materials. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welders provide precise control and clean welds, particularly valuable for detailed work. Stick welders, while basic, remain reliable for outdoor projects and thick materials, offering excellent durability in challenging conditions.
Essential Metal Fabrication Equipment Considerations
When selecting welding equipment, power requirements and duty cycle are critical factors. Single-phase machines (110V/220V) suit most home workshops, while three-phase units (480V) are standard in industrial settings. The duty cycle indicates how long a machine can operate continuously before requiring cooldown. Professional-grade machines typically offer higher duty cycles, ensuring sustained operation for demanding projects.
Welding Safety Training Requirements
Safety remains paramount in welding operations. Proper training should cover personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, including auto-darkening helmets, heat-resistant gloves, and flame-resistant clothing. Understanding ventilation requirements and electrical safety is essential. Most manufacturers and technical schools offer comprehensive safety courses, often combining classroom instruction with hands-on practice.
Setting Up Your Home Workshop Welding Space
Creating an effective home welding workspace requires careful planning. Essential elements include proper ventilation systems, fire-resistant surfaces, and adequate electrical capacity. A minimum workspace of 100 square feet allows comfortable movement while welding. Storage solutions for materials and tools, plus a dedicated grinding area, help maintain organization and safety.
Mastering Beginner Welding Techniques
Successful welding starts with mastering fundamental techniques. Proper joint preparation, including cleaning and beveling edges, significantly impacts weld quality. Understanding amperage settings, travel speed, and electrode angles helps achieve consistent results. Beginning welders should practice on scrap material before attempting project work.
| Welding Machine Type | Suitable Applications | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| MIG Welder (Entry) | Home/Light Commercial | $300-$800 |
| TIG Welder (Basic) | Precision Work | $800-$2,000 |
| Stick Welder | Outdoor/Heavy Duty | $200-$500 |
| Multi-Process | Versatile Use | $1,000-$3,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The welding machine market continues to evolve with technological advancements, offering improved efficiency and user-friendly features. Whether choosing equipment for home projects or industrial applications, understanding machine capabilities, safety requirements, and proper technique fundamentals ensures successful welding operations. Regular maintenance and adherence to manufacturer guidelines help maximize equipment lifespan and performance.